Functions of the Control Unit
Functions of the Control Unit
1.Instruction Fetching
2.Instruction Decoding
3.Control Signal Generation
4.Sequencing
5.Data Movement
6.Branching and Jumping
7.Exception Handling
8.Clock Synchronization
9.Microcode Execution
EXPLAIN All of Headings
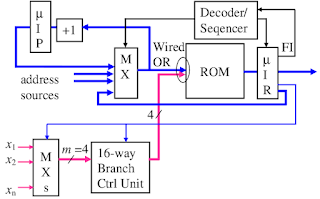
1.1.Instruction Fetching
This stage involves fetching the next instruction from memory. The program counter (PC) holds the address of the next instruction to be fetched. The fetched instruction is stored in the instruction register (IR).
1.2 Instruction Decoding
In this stage, the fetched instruction (from the IR) is decoded to determine the operation to be performed. This stage identifies the opcode and any operands required for the instruction.
1.3 Control Signal Generation
Control signals are generated based on the decoded instruction. These signals control various components in the CPU, such as ALU operations, memory access, and data movement.
1.4 Sequencing
This stage manages the order in which instructions are executed. It ensures that instructions are executed in the correct sequence and handles the transfer of data between stages.
1.5 Data Movement
Data movement involves transferring data between registers, memory, and other components. It includes operations like loading data from memory to registers or storing data from registers to memory.

.png)

.jpg)


.png)





Comments
Post a Comment